Bridging the Gap: Integrating COVID-19 Services into Primary Healthcare
This article discusses the integration of COVID-19 services into primary healthcare, highlighting the disparities revealed by the pandemic and the need for Test & Treat programs. The approach emphasizes early diagnosis and treatment, focusing on equity and community outreach. Various initiatives and guidelines are being developed to support these efforts, aiming to create more resilient health systems for future health crises.
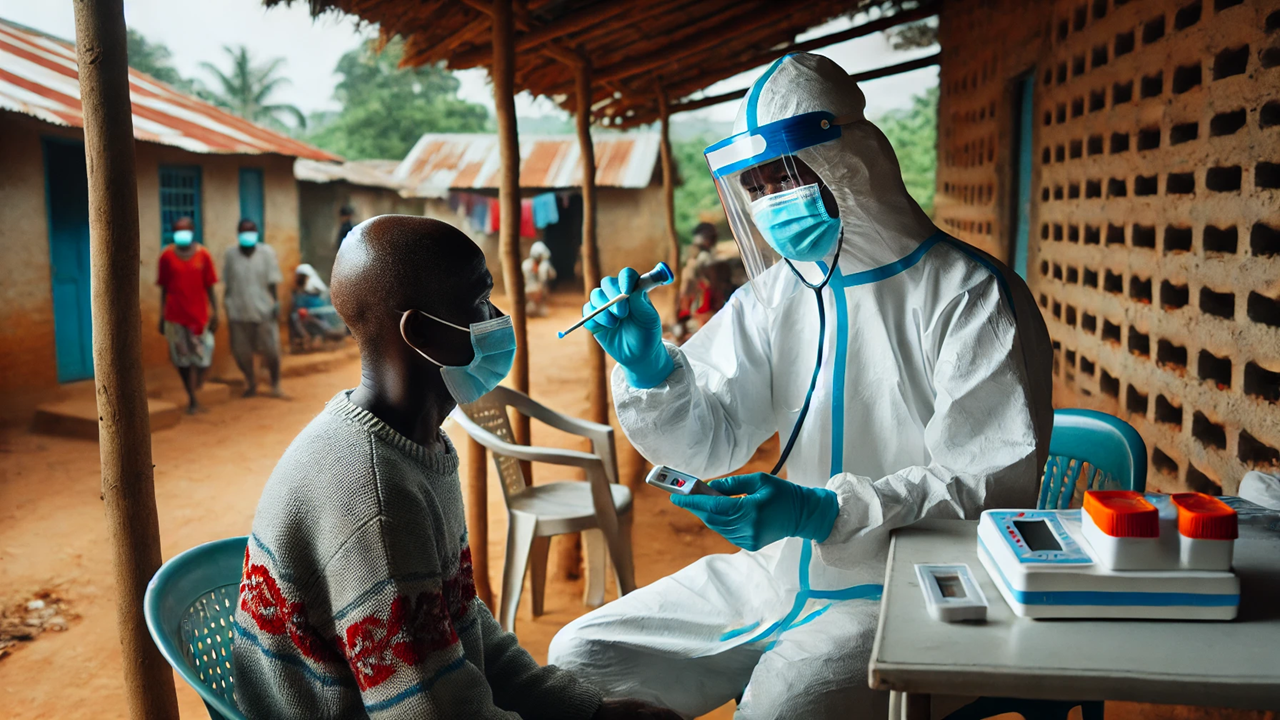
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, global health disparities were thrust into the spotlight, revealing significant inequities in access to medical services. A recent report by Partners In Health, titled "Test and Treat: Integration of COVID-19 Services into Primary Healthcare," highlights these challenges and outlines the need for comprehensive Test & Treat programs to manage the pandemic and future health crises.
The Stark Reality of Health Inequities
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a powerful lens through which the world has seen the deep-seated inequities in global healthcare. As of September 2023, the World Health Organization reported over 770 million confirmed cases and nearly 7 million deaths worldwide. The pandemic's impact has been disproportionately severe on marginalized and impoverished communities, where access to essential services such as testing, therapeutics, and vaccines remains limited.
Globally, the distribution of COVID-19 tests has been alarmingly uneven. Between March 2020 and April 2023, only 0.4% of the over 6 billion COVID-19 tests were administered in low-income countries, despite these nations accounting for over half of the global population. This disparity underscores the urgent need for robust Test & Treat programs that can provide equitable healthcare solutions.
Lessons from the Frontlines
The implementation of Test & Treat programs during the pandemic faced numerous obstacles, ranging from limited testing accessibility and supply chain issues to regulatory and intellectual property barriers for therapeutics. The lack of focus on outpatient care and delays in approving self-testing further compounded these challenges.
In many low- and middle-income countries, the situation was exacerbated by a lack of manufacturing capabilities and high costs of testing. For example, while the cost of a COVID-19 test in some European countries could be as low as $1, prices remained prohibitively high in many parts of the world.
Test & Treat: A Proven Strategy
The Test & Treat approach emphasizes early diagnosis and outpatient treatment to prevent disease progression, complications, and transmission. This strategy is not new; it has been successfully implemented in programs for HIV, malaria, and tuberculosis. By integrating Test & Treat within existing health systems, the approach aims to ensure equity and person-centered care.
The importance of a robust Test & Treat strategy cannot be overstated. It has the potential to reduce hospital admissions, save lives, protect vulnerable populations, and build community trust. Moreover, it offers spillover benefits to other health interventions and helps in the early identification and containment of outbreaks.
Building on Existing Efforts
Several initiatives have already begun to implement Test & Treat programs. The COVID Treatment QuickStart Consortium and USAID's Test-To-Treat programs focus on providing antiviral therapies and enhancing primary care capacities. Despite these efforts, comprehensive guidelines from the World Health Organization (WHO) on Test & Treat for COVID-19 are still in development.
Successful Test & Treat programs must focus on primary care and rural systems, community outreach, free and routine testing, self-testing, and rapid linkage to treatment. They should also incorporate triage for severe cases and integrate with public health services.
Looking Ahead: Monitoring and Evaluation
To ensure the success of Test & Treat programs, it is crucial to track several key indicators, including the number of people tested, positivity rates, timeliness of testing, treatment eligibility, linkage to treatment, treatment completion, long COVID symptoms, and budget allocation. Early data collection and sharing can help policymakers and implementers refine these programs to better serve their populations.
The operational guidance from Partners In Health lists various resources, guidelines, and tools from WHO, USAID, and other organizations to support the implementation of Test & Treat programs.
The integration of COVID-19 services into primary healthcare is a critical step toward addressing the global health inequities exposed by the pandemic. By building on the Test & Treat model, we can create more resilient health systems that are better equipped to handle future health crises. The efforts of organizations like Partners In Health, WHO, and USAID are paving the way for a more equitable and effective global health response.
- FIRST PUBLISHED IN:
- Devdiscourse
ALSO READ
Digvijaya Singh Tests Positive for COVID-19 Again
South Korea Faces Possible ER Crisis Amidst Doctor Strike and COVID-19 Surge
Zuckerberg Alleges Government Pressure to Censor COVID-19 Content
Indian Immunologicals Develops Intranasal COVID-19 Vaccine
Govt Finalizes Terms for Phase 2 of COVID-19 Royal Commission of Inquiry










