Sun releases powerful X-class solar flare: Should we worry?
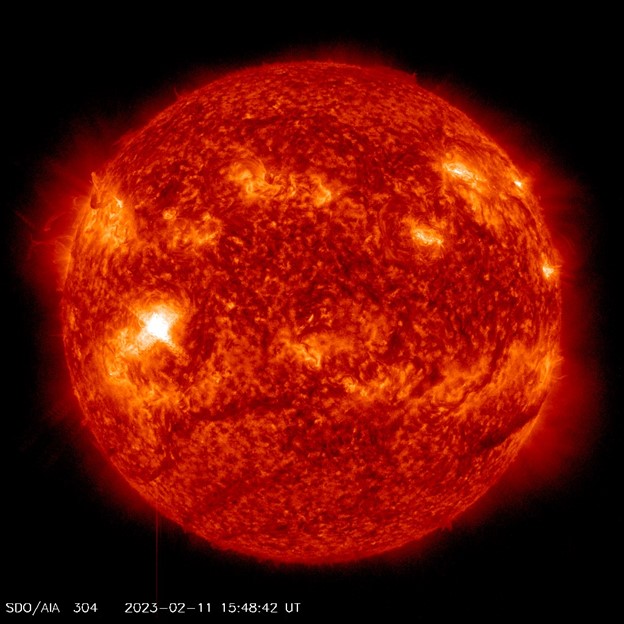
The Sun released a powerful solar flare - a sudden and intense burst of energy from the sun's surface - on February 11, which peaked at around 10:48 a.m. EDT, according to NASA.
A picture of this event was captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) which keeps a constant eye on the Sun. This flare was classified as an X1.1 flare.
For the unversed, solar flares are classified into three categories based on their strength: C-class, M-class, and X-class, with X-class being the strongest. The number provides more information about the flare's strength.
The Sun emitted a strong solar flare on Feb. 11, 2023, peaking at 10:48 a.m. ET. NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory captured an image of the event, which was classified as X1.1. https://t.co/R3S2hRt4Zd pic.twitter.com/AcZtXaLwxv
— NASA Sun & Space (@NASASun) February 13, 2023
Should we worry?
While harmful radiation from a solar flare cannot pass through Earth’s atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, when intense, it can disrupt communications systems, navigation signals, and power grids. The flares also release large amounts of high-energy particles and electromagnetic radiation into space, which can pose a danger to astronauts and spacecraft.
It's worth mentioning that the Sun is approaching Solar Maximum - the point in its natural 11-year cycle when it reaches its highest level of activity. During this period, the sun's magnetic fields become more chaotic and unstable, resulting in an increased number of sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
In the past week alone, the Sun unleashed 20 solar flares and 34 coronal mass ejections
Happy #SunDay! This week’s space weather report includes 20 notable solar flares, 34 coronal mass ejections, and no geomagnetic storms. This video from NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory shows an M6 flare from February 7 around 2 minutes in. pic.twitter.com/qPMHUtzcin
— NASA Sun & Space (@NASASun) February 12, 2023
- READ MORE ON:
- solar flares
- solar maximum
- NASA










