Building Resilient Health Systems: A Three-Layer Approach to Pandemic Preparedness
A three-layer framework emphasizes prevention, rapid response, and advanced care to build resilient health systems, focusing on cost-effective early interventions to mitigate future pandemics. This approach advocates for holistic health system strengthening to ensure preparedness for various health challenges.
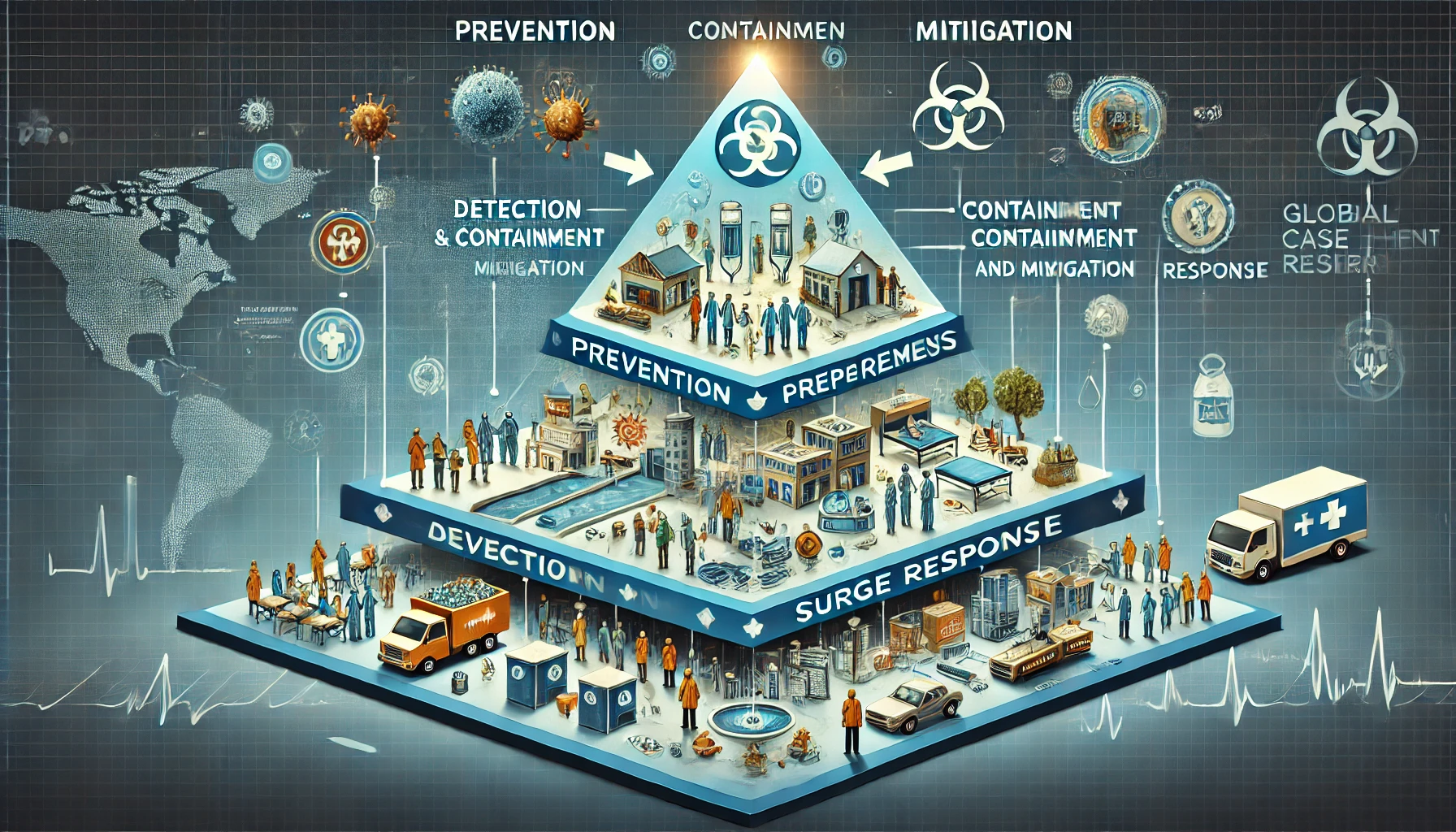
A study by World Bank edited by Feng Zhao, Rialda Kovacevic, David Bishai, and Jeff Weintraub, proposes a strategic approach to strengthening global health systems in preparation for future pandemics. The publication advocates for a three-layer framework designed to enhance health systems by focusing on prevention, rapid response capabilities, and advanced care management. This framework is essential for countries aiming to build resilience against health threats, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, which exposed significant weaknesses in global health systems.
Building Resilience Through Prevention and Preparedness
At the heart of the framework is the idea that the most effective way to protect populations from health threats is to prevent those threats from emerging in the first place. This is where the first layer, risk reduction through prevention and community preparedness, comes into play. It involves establishing robust primary health care systems that are widely accessible and capable of delivering essential public health services. These services include early-warning systems, strong surveillance mechanisms, and the promotion of healthy behaviors through education and community engagement. The focus is on preventing diseases at the community level, which requires a well-coordinated effort involving public health institutions, health care providers, and community leaders. The publication emphasizes that investments in this layer are critical because they lay the groundwork for a resilient health system that can respond effectively to health threats before they escalate into full-blown crises.
Effective Detection and Containment as a Second Defense
The second layer of the framework addresses the need for effective detection, containment, and mitigation capabilities. This layer is activated when a health threat is identified, and it involves scaling up testing, isolating suspect cases, and implementing measures such as quarantine, social distancing, and contact tracing. These interventions are designed to limit the spread of infectious diseases and protect at-risk populations. The publication highlights that this layer is crucial for containing outbreaks and preventing them from becoming widespread pandemics. By investing in the tools and infrastructure needed to detect and respond to health threats early, countries can significantly reduce the impact of these threats on their populations and health systems.
Advanced Care for Critical Cases
The third layer of the framework focuses on advanced case management and surge response. This layer includes secondary and tertiary care facilities that provide critical care during health crises. While this layer is essential for managing severe cases and saving lives during pandemics, it is also the most costly and resource-intensive. The publication points out that relying heavily on this layer, as was the case during the COVID-19 pandemic, is not a sustainable or effective strategy. Instead, the emphasis should be on strengthening the first two layers, which can prevent the need for large-scale reliance on advanced care facilities. The World Bank's framework underscores that investments in prevention and early response are far more cost-effective than focusing solely on advanced treatment. By preventing health crises before they escalate, countries can avoid the enormous economic and social costs associated with hospitalization and intensive care.
Beyond Pandemics: A Holistic Approach to Health Systems
The publication also discusses the broader implications of the three-layer framework for health systems. It argues that the framework is not only applicable to pandemic preparedness but also to the overall functioning of health systems. By strengthening the foundational elements of health systems, such as primary care and public health services, countries can improve their ability to manage a wide range of health challenges, from infectious diseases to non-communicable conditions like heart disease and diabetes. The framework encourages countries to adopt a holistic approach to health system strengthening, integrating public health functions with service delivery to create a more resilient and responsive system.
The Urgency of Investing in Health System Resilience
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a wake-up call for the global community, highlighting the urgent need for stronger health systems. The World Bank's three-layer framework offers a clear and actionable path for countries to follow as they work to build resilience against future health threats. The publication urges countries to take proactive steps now to invest in their health systems, emphasizing that the costs of inaction are far higher than the costs of prevention and preparedness. By adopting this framework, countries can protect their populations, safeguard their economies, and ensure that they are better prepared for the health challenges of the future. The key takeaway is that while it may be tempting to focus on short-term crisis management, the real gains come from investing in long-term resilience through strategic and systematic health system strengthening.
- FIRST PUBLISHED IN:
- Devdiscourse
ALSO READ
Global Health Updates: Mpox Vaccinations, COVID Shots, and More
Global Health Update: Polio and Mpox Vaccinations, Bird Flu Impact
Global Health News: Major Updates on Mpox, COVID-19, Polio, and Oropouche Virus
UNICEF's Emergency Efforts and Global Health Trends
Obesity, Ozempic Shortages, and Global Health Crises: Current Health News Analysis










