Can blockchain rescue from supply chain disruptions due to COVID-19?
Blockchain significantly increases transparency by providing real-time data access to all participants across the entirety of the supply chain whilst reducing the need for intermediaries.

The mandatory containment measures including social distancing, trade restrictions to mitigate the threats of COVID-19 pandemic is not only impacting individual lives but is also putting a strain on the global economy with leading economic institutes predicting a deep and long-lasting recession.
The worldwide shutdown of factories and businesses, followed by the unprecedented surge in demand for certain goods, particularly groceries and medical supplies, has strained the supply chain networks. Manufacturers and suppliers are scrambling to continue operations to cater to the increasing or decreasing demand amidst the pandemic.
According to a survey conducted by the Institute for Supply Management (ISM) on COVID-19 global supply chain disruptions, in early March, six percent of respondents reported severe disruptions and more than 80 percent believed that their organization would experience some impact from COVID-19 disruptions. By the March-end, this increased to 95 percent of organizations that were already impacted or would be as a result of the pandemic.
The corona crisis has already exposed the weaknesses of our overwhelmed supply chain networks and underscored the importance of interconnectedness and transparency to keep them moving in any environment. More and more businesses and their supply chains are now exploring innovative solutions to navigate through the crisis and prepare for the new normal.
Blockchain, the underlying technology behind digital currencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, is one such nascent technology that can be a game-changer for the overall supply chain management as it enables information sharing in near real-time and enhances transparency, traceability, and operational efficiency of supply chains whilst reducing the need for intermediaries and hence physical proximity.
The nascent technology has already revolutionized the financial sector and also holds immense potential for managing global supply chains which involve diverse actors including suppliers, manufacturers, transporters, retailers, and consumers.
How can blockchain help address supply-chain issues?
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed, and public digital ledger technology that stores all transactions in blocks, each of which has a unique hash, a cryptographic function to secure the data, of the previous block which makes it extremely difficult for anyone who attempts to manipulate the data. Normally, supply chain operations begin with sourcing the raw materials and end with the delivery of finished products to the consumers. However, lack of coordination, trust, and end-to-end visibility along the chain make it difficult for stakeholders to manage through the supply chain disruption. With blockchain, all parties involved in the chain are given full real-time access to data which is critical to building trust, collaboration among the entities and participants whilst simultaneously increasing the efficiency and transparency of supply chains.
 Figure: Supply chain participants
Figure: Supply chain participants
For example, in view of the COVID-19 induced supply disruptions, IBM recently launched a blockchain-based network that works as a digital passport for supplier management. The IBM Rapid Supplier Connect is purposely designed to help organizations and government agencies quickly find critical supplies and services in an unconventional marketplace with greater efficiency. Using the network, buyers can benefit from new and non-traditional suppliers, a streamlined supplier onboarding process, validation checks, and inventory information in near-real-time while suppliers can benefit from a portable online identity, access to user feedback, and the ability to post and manage inventory availability. The network is freely available to qualified buyers and suppliers through August 31, 2020, to help responders battle the COVID-19 pandemic.
Here is are the key benefits that the blockchain technology offers to improve supply chain management and future resiliency.
Enhanced transparency
With blockchain, each participant across the supply chain is visible and every transaction is recorded on a shared ledger. All independent actors can store, view, and share the supply chain data, subsequently increasing transparency, accountability, and trust.
For instance, the BMW Group, the world’s leading premium manufacturer of automobiles, which is using the blockchain technology to drive transparency and traceability of components and raw materials in multi-stage and highly complex international supply chains. The group's PartChain project enables tamper-proof and consistently verifiable collection and transaction of data in its supply chain.
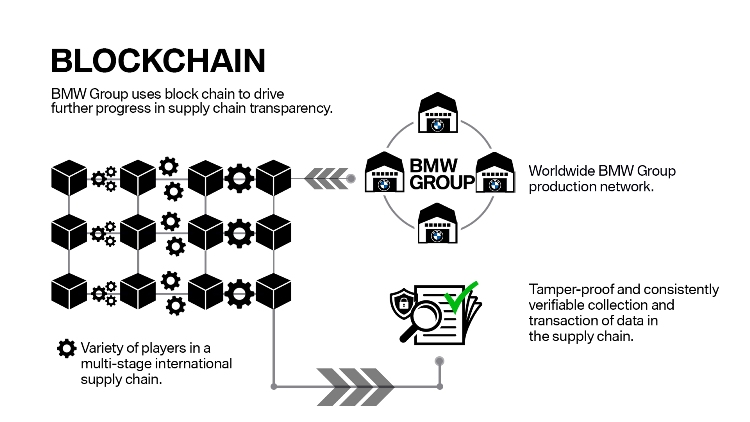 Image Credit: BMW Group
Image Credit: BMW Group
Real-time traceability
Blockchain dramatically increases the real-time data traceability of the material supply chain by providing full transparency into the origin of raw material or components.
For instance, French retailer Carrefour SA has deployed a blockchain solution to trace the entire production chain of more than 25 items including fresh Norwegian salmon Carrefour Quality Line (FQC), farmed chicken, Camembert, fresh milk, etc. Consumers can use their smartphones to track the product's journey from the place of farming to its shelving.
Fraud reduction
If we take the current situation into account, the public health crisis has also sparked a new trend in the online sale of unauthorized and counterfeit medical devices and products like corona self-testing kits, face masks, and antiviral medication. In March, INTERPOL member countries conducted Operation Pangea XIII that resulted in the seizure of more than 34,000 counterfeit and substandard items related to COVID-19, including potentially dangerous pharmaceuticals worth more than USD 14 million.
This is where blockchain comes into the picture. With increased transparency and real-time traceability, blockchain can help prevent fraud in the supply chains. Also, the information captured in each transaction can be altered or deleted only through a consensus among the network participants.
The global pharmaceutical industry has been struggling too long to stop the illegal trading of drugs, vaccines, etc., prompting it to explore the potential of blockchain technology to enhance the safety and security of the drug supply chain. For instance, tech giant IBM, Merck, and Walmart, last year, proposed a project to assess if the blockchain technology can help address the need of the pharmaceutical supply chain. The pilot project is part of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) program that seeks to examine new technologies, processes, or methods for enhanced requirements outlined in the U.S. Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) for 2023.
According to the consortium's Blockchain Interoperability Pilot Project report, the proposed solution could provide a common record of product movement, from the point of commissioning to the point of dispense, by connecting disparate systems and organizations to meet DSCSA 2023 interoperability requirements in a secure way. In addition, the solution takes a few seconds to triggers alerts and increase visibility to relevant supply chain partners in the event of a product investigation or a manufacturer-generated recall which could otherwise take as much as three days.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts on a blockchain are digital and automated lines of code based on predetermined conditions that execute transactions without the involvement of an intermediary. They drive business efficiency by automating procedures that otherwise need manual efforts.
For example, recently, Mexico's Toks Restaurant Chain collaborated with blockchain innovator SIMBA Chain to develop a blockchain-enabled prototype that will help it gain greater visibility and traceability in its supply chain. SIMBA Chain's smart contract solution will help Toks to register and track coffee beans purchased, processed, packaged, and sold by the restaurant chain.
Barriers to widespread adoption
Despite the immense potential blockchain holds for various industries including supply chains and logistics, there are various factors preventing its widespread adoption. One major challenge to its adoption is its technical scalability, meaning it can process very few transactions as compared to legacy transaction networks that can process thousands of transactions per second. VISA, for example, says its network is capable of handling more than 24,000 transactions per second as compared to bitcoin, the first use case of blockchain technology, that can process only 3-7 transactions per second.
Another issue is the lack of interoperability among different blockchain networks that operate on silos and avoid sharing information. However, there are many efforts underway to enable an interoperable network of blockchains and other issues hampering its widespread adoption.
For businesses looking to deploy this technology, the World Economic Forum (WEF) recently launched a Blockchain Deployment Toolkit to help them explore key success and risk factors within the supply chain context. The Toolkit provides tools, resources, and guidelines that can streamline blockchain implementation efforts for a diverse range of supply chains and their stakeholders ensuring continued resilience.
The challenge is not about identifying the right blockchain technology for the specific need, it’s about providing the supportive structure around to adapt it - a challenge we see coming to the surface clearly in today’s COVID-19 world. And, with over four trillion consumer products made and shipped around the world each year, we cannot afford to continue operating in the dark when it comes to keeping track of these products -especially when some of these products could save lives. - World Economic Forum
While blockchain itself is not a complete package for an effective supply chain management, but it can play a significant role in transforming them, especially when it comes to handling highly-complex networks involving multiple entities and participants.
Centre of Excellence on Emerging Development Perspectives (COE-EDP) is an initiative of VisionRI and aims to keep track of the transition trajectory of global development and works towards conceptualization, development, and mainstreaming of innovative developmental approaches, frameworks, and practices.
- FIRST PUBLISHED IN:
- Devdiscourse

 COE-EDP
COE-EDP









