This monster star blew its top in 2019; still slowly recovering from catastrophic upheaval
What happens after a supergiant star blows its top?
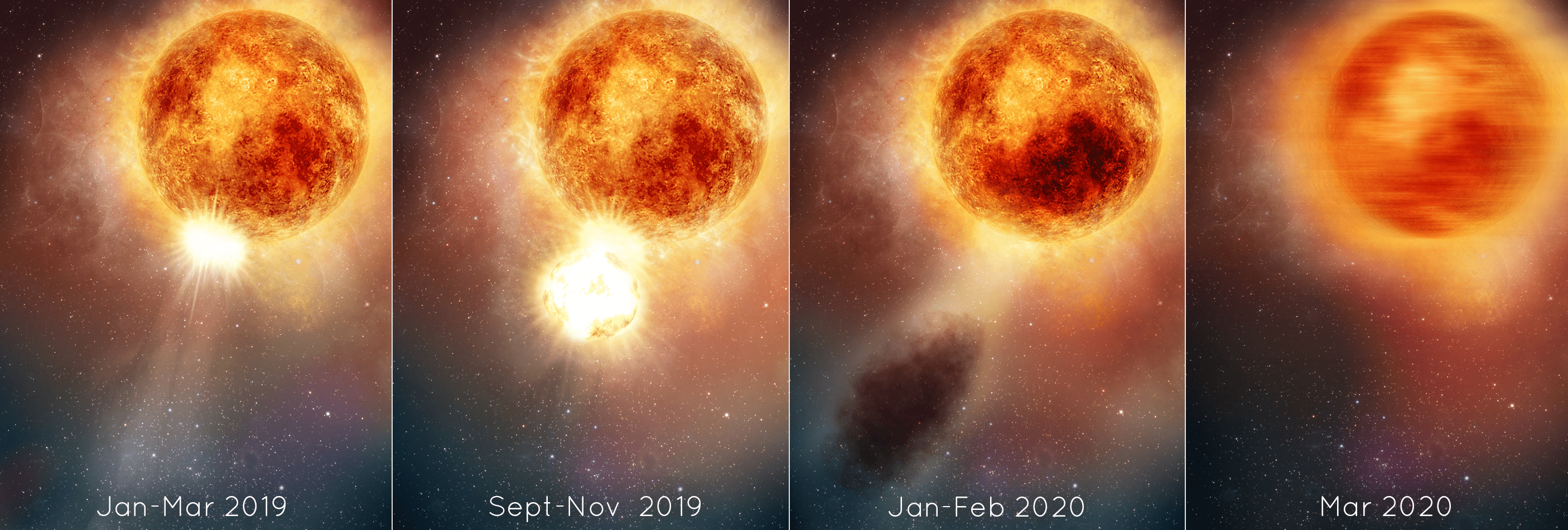
The bright red supergiant star Betelgeuse quite literally blew its top in 2019, producing a gigantic Surface Mass Ejection (SME). The star is still struggling to recover from this titanic convulsion.
Betelgeuse is one of the brightest stars in the sky and is easily found in the right shoulder of the constellation Orion. The monster star blasted off 400 billion times as much mass as a typical Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) - large expulsions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun's outer atmosphere - the Corona.
The astronomers analysed new spectroscopic and imaging data from the STELLA robotic observatory, the Fred L. Whipple Observatory's Tillinghast Reflector Echelle Spectrograph (TRES), NASA's Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory spacecraft (STEREO-A), NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, and the American Association of Variable Star Observers (AAVSO) to draw this conclusion.
"We've never before seen a huge mass ejection of the surface of a star. We are left with something going on that we don't completely understand. It's a totally new phenomenon that we can observe directly and resolve surface details with Hubble. We're watching stellar evolution in real-time," said Andrea Dupree of the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian in Cambridge, Massachusetts, emphasising that the Hubble data was pivotal to helping sort out the mystery.
Betelgeuse, Betelgeuse, Betelgeuse…This supergiant star experienced a huge mass ejection of its visible surface back in 2019 – something never before seen in a normal star’s behavior.Hubble observations are giving clues about this stellar mystery: https://t.co/iyfQbYt0Bt pic.twitter.com/bfsqX0iGrZ
— Hubble (@NASAHubble) August 11, 2022
According to the researchers, the outburst was possibly caused by a convective plume, more than a million miles across, bubbling up from deep inside the star. The explosion produced shocks and pulsations that blasted off the chunk of the photosphere. The fractured piece of photosphere sped off into space and cooled to form a dust cloud that blocked light from the star as seen by Earth observers.
More details can be found here.










