Breakthrough in Parkinson’s Research: Nano-Melatonin Shows Enhanced Neuroprotective Properties
Recent studies have identified the significance of mitophagy, a quality control process that removes dysfunctional mitochondria to mitigate oxidative stress.
- Country:
- India
Researchers have demonstrated that a nano-formulation of melatonin, a hormone secreted by the brain in response to darkness, exhibits improved antioxidative and neuroprotective properties. This discovery could pave the way for a novel therapeutic approach to managing Parkinson’s disease (PD), one of the most prevalent neurological disorders.
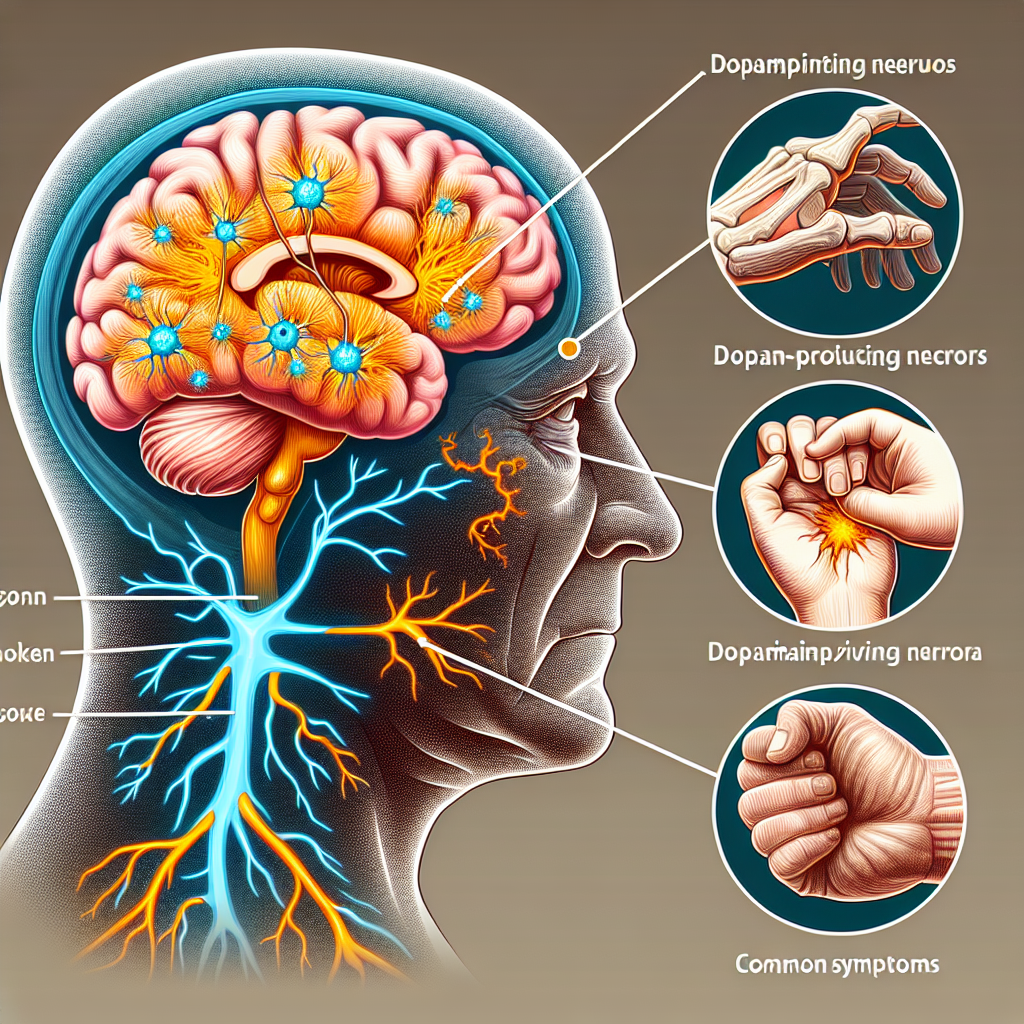
Parkinson’s disease arises from the death of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, largely due to the aggregation of synuclein protein. Current treatments only alleviate symptoms, underscoring the need for more effective therapies.
Recent studies have identified the significance of mitophagy, a quality control process that removes dysfunctional mitochondria to mitigate oxidative stress. Melatonin, a neurohormone known for regulating sleep cycles, has shown potential as an inducer of mitophagy. However, challenges such as low bioavailability and difficulty in brain delivery have limited its therapeutic efficacy.
Nano-Formulation: A Game-Changer
A research team from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, has developed a human serum albumin (HSA) nano-formulation to enhance melatonin delivery to the brain. This innovative approach demonstrated:
- Sustained Release of Melatonin: Improving bioavailability.
- Targeted Brain Delivery: Enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
The nano-melatonin formulation was tested in an in vitro PD model using rotenone, a pesticide that induces mitochondrial toxicity. Results revealed significant improvement in both mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis, which are critical in combating neurodegeneration. Key Findings and Mechanisms:
Epigenetic Regulation via BMI1
The study uncovered that nano-melatonin upregulated BMI1, a critical epigenetic regulator in the Polycomb Repressive Complex 1. This overexpression:
- Induced mitophagy to remove unhealthy mitochondria.
- Reduced oxidative stress, a major contributor to PD pathology.
- Protected neurons from degeneration in both in vitro and in vivo models.
Neuroprotective Outcomes
The formulation protected TH-positive neurons in rat brains against rotenone-mediated toxicity. Enhanced mitophagy and antioxidative effects contributed to mitigating PD symptoms.
Implications for Parkinson’s and Beyond
This research provides a molecular explanation for melatonin’s role in mitophagy regulation. The findings open doors for melatonin’s application in treating other diseases linked to dysfunctional mitophagy, such as Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s diseases.
Published Findings
The team’s research, published in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, highlights the superior neuroprotective effects of nano-melatonin. The results reinforce its potential as a safer, more effective treatment option for PD and related neurodegenerative disorders.
Future Directions
This breakthrough highlights the promise of nano-melatonin as a therapeutic candidate for Parkinson’s disease. With further exploration, it could establish itself as a reliable, accessible treatment to improve the lives of millions worldwide.
- READ MORE ON:
- Parkinson’s
- mitophagy










